How to Grab a Pull Request Locally with Git Command Line
Date Published: 29 July 2019
If you're working with git, especially with open source, sometimes you'll find that you want to work with a particular pull request, or PR, locally. Maybe you're reviewing the PR and instead of just eyeballing it in the browser you want to actually run the code and see what it does (novel idea, I know!). In any case, actually getting the code from a PR, especially one from a fork that isn't even in your codebase, isn't necessarily as simple as just checking out a branch. Here's a quick bit of code you can use to do it:
git fetch REMOTE pull/PRNUMBER/head:BRANCHNAME
EXAMPLE:
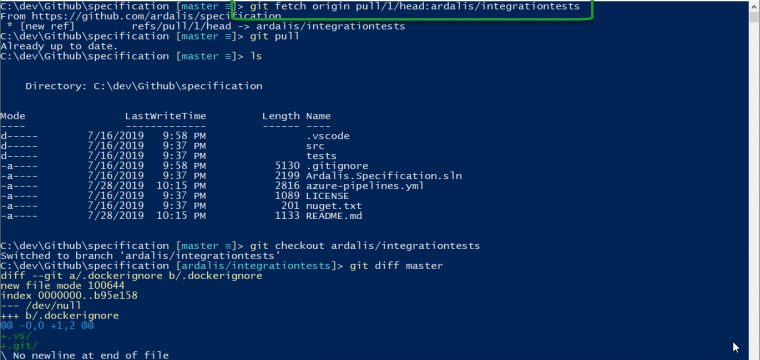
git fetch origin pull/1/head:ardalis/integrationtestsIn the above example (and screenshot), I'm fetching this pull request to my Ardalis.Specification open source nuget package repository. I've already cloned the repo locally, so my remote is origin but sometimes this might be upstream or another remote in your situation. If you want to see a list of remotes you have defined for your local git repo, run git remote -v.
Next, you need to specify the PR number, that's the 1 after pull/ in my example. And then add in /head: followed by your branch name. In my case my branch name is ardalis/integrationtests. I typically format my branches as username/description so that I can easily find my branches in a repo when it's time for me to clean them up, etc. Many git clients will collapse branches in a treeview if you use this approach.
That's about it. Please add a comment if you have any questions. Once you have this working, you can use git checkout BRANCHNAME to actually switch to the PR and test it, run git diff against it, etc.
Oh and one last tip if you're using PowerShell. You probably know you can clear the screen with clear but that adds a command to your command history. You can also clear it with ctrl-L which does not add a command to your history.
Using the GitHub CLI
If you install the GitHub CLI (command line interface), you can do this much more easily using just this command:
# List all PRs
gh pr list
# Check out PR #123
gh pr checkout 123I recorded a video detailing the GitHub command line with John Papa here:
Category - Browse all categories

About Ardalis
Software Architect
Steve is an experienced software architect and trainer, focusing on code quality and Domain-Driven Design with .NET.
