Hello, Redis - Getting Started with Redis and dotnet 8
Date Published: 11 February 2024

Integrating Redis Caching in .NET 8 Applications
Redis is an open-source, in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache, and message broker. It's known for its speed and flexibility, making it an excellent choice for caching in modern applications. In this article, we'll explore how to use Redis for caching in a .NET 8 application, covering both setting up Redis using Docker on a Windows development machine and integrating it into your .NET application.
Setting Up Redis with Docker on Windows
Before diving into the .NET integration, it's essential to have Redis available for development. For those without Redis installed on their Windows development machine, Docker provides a clean and straightforward way to run Redis. Here's how to set it up:
Install Docker Desktop for Windows
First, download and install Docker Desktop for Windows. Follow the installation guide, ensuring the WSL 2 feature is enabled if prompted.
Start Docker Desktop
Launch Docker Desktop and wait for it to indicate that it's running. This setup might take a few minutes initially.
Run Redis Container
Open a terminal window and execute the following command to run Redis in a Docker container:
docker run --name my-redis -p 6379:6379 -d redisThis command does the following:
--name my-redis: Names the container for easy reference.-p 6379:6379: Maps the default Redis port, 6379, from the container to your local machine.-d: Runs the container in detached mode.redis: Uses the Redis image from Docker Hub.
Verify the Redis Container
Ensure the Redis container is running with:
docker psIf you need to stop redis, you can run docker stop {container_id} where the container_id is shown in the above docker ps command.
You should see my-redis listed among the running containers.
Integrating Redis in a .NET 8 Application
With Redis running, let's integrate it into a .NET 8 application using the StackExchange.Redis NuGet package, a high-performance Redis client.
Create a .NET 8 Application
Create a new console application:
dotnet new console -n HelloRedis
cd HelloRedisAdd the StackExchange.Redis Package
Install the StackExchange.Redis package:
dotnet add package StackExchange.RedisThis will install the latest version from Nuget.org.
Implement Redis Cache Logic
Replace the content of Program.cs with the following code to connect to Redis and serialize/deserialize objects:
using StackExchange.Redis;
using System.Text.Json;
Console.WriteLine("Run this command to start redis in docker:");
Console.WriteLine("docker run --name my-redis -p 6379:6379 -d redis");
// Connection to Redis server - make sure it's running in Docker!
var redis = ConnectionMultiplexer.Connect("localhost");
var db = redis.GetDatabase();
var user = new User { Id = 1, Name = "John Doe", Email = "johndoe@example.com" };
// Serialize the User object to a JSON string.
string userJson = JsonSerializer.Serialize(user);
// Store the serialized User object in Redis with the key "user:1".
await db.StringSetAsync("user:1", userJson);
Console.WriteLine("User object stored in Redis.");
// Fetch the serialized User object from Redis.
string? fetchedUserJson = await db.StringGetAsync("user:1");
// If not found end program
if (fetchedUserJson is null)
{
Console.WriteLine("User object not found in Redis.");
return;
}
// Deserialize the JSON string back to a User object.
var fetchedUser = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<User>(fetchedUserJson);
// If not found end program
if (fetchedUser is null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"User object failed to deserialize from json:\n {fetchedUserJson}.");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine($"Fetched User: {fetchedUser.Name}, Email: {fetchedUser.Email}");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.WriteLine("If you got this far and you see the user name and email above, it worked!");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
You'll also want to create a User class either in the same file or a new one:
public class User
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; } = string.Empty;
public string Email { get; set; } = string.Empty;
}Running Your Application
Execute your application with:
dotnet runYou should see the following:
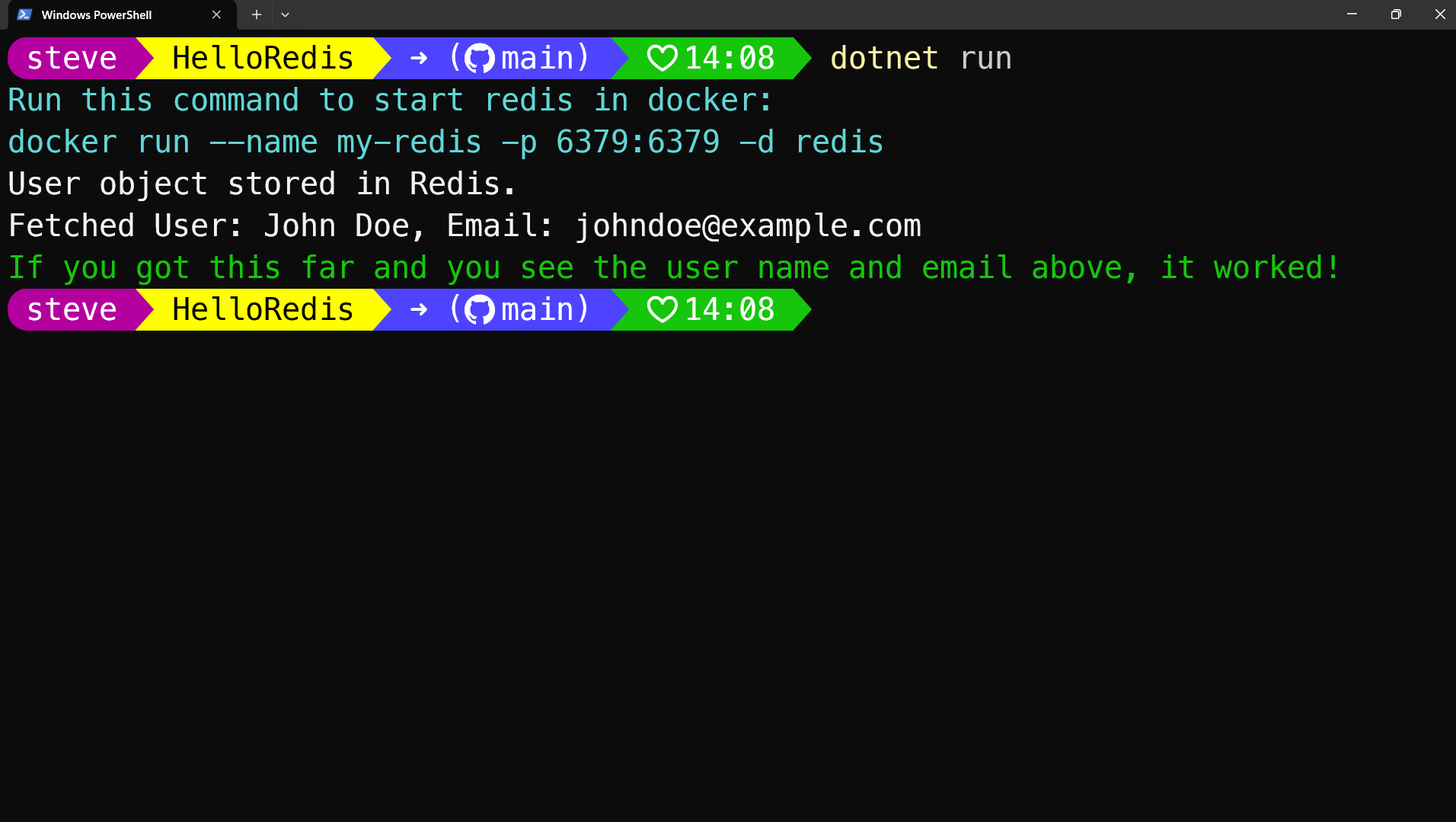
This example demonstrates storing and retrieving an object in Redis, utilizing serialization for object handling.
GitHub Repo
You can view the latest version of this article's code in the associated GitHub repository. Feel free to add issues or pull requests there.
Conclusion
Integrating Redis into your .NET 8 applications provides a robust caching mechanism, enhancing performance and scalability. Docker simplifies managing your Redis instance, keeping your development environment clean and straightforward. This guide has covered the essentials to get you started with Redis and .NET 8, including setup, implementation, and basic operations.
Keep Improving!
P.S. If you're looking to improve as a software developer, you may wish to join thousands of other developers who get my newsletter each week. Sign up here!
Category - Browse all categories

About Ardalis
Software Architect
Steve is an experienced software architect and trainer, focusing on code quality and Domain-Driven Design with .NET.
